Calculation of elevation from horizontal distance and inclination angle with allowance for measurement error
This online calculator allows you to calculate the elevation from horizontal distance and inclination angle taking into account the mean square errors of measurements.
The calculation formulas are shown below the calculator
Calculation of elevation
In the figure below, the following notations are used:
- S - line length
- D - horizontal line projection, i.e. projection of the terrain line on a horizontal plane.
- h - elevation, i.e. height difference of one point relative to another point
- γ - angle of inclination of the line to the horizon
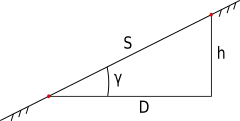
From fairly obvious geometric considerations, the elevation can be expressed in terms of horizontal distance and the angle of inclination to the horizon by the following formula:
.
Mean square error of measurement
The accuracy of measurement is characterised by the mean square error of measurement (MSE). For quantities measured explicitly, the MSE is usually known. Elevation is measured indirectly, in this case, its value is calculated as a function of horizontal distance and inclination angle.
The general formula for the dependence of the MSE of the function calculation result on the MSE of its arguments is as follows:
If the quantity is computed as a function of the arguments
characterised by the MSE
:
then the MSE of the calculated quantity is equal to:
where is the partial derivative of the function on the variable
. Index 0 means that the numerical value of the partial derivative obtained after substituting the numerical values of the arguments is taken.
In the case of the function we have
The inclination angle and the MSE of the inclination angle must be expressed in radians.
This is the formula used in the calculator to determine the MSE of the elevation.
Comments